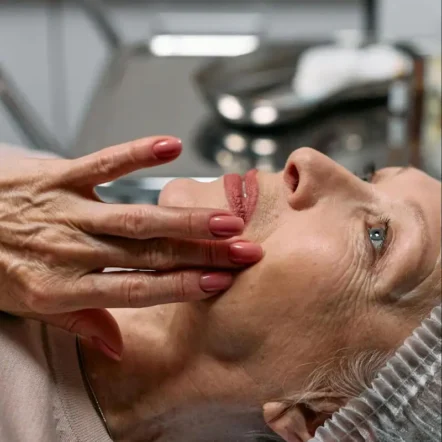
Condition
Pigmentation
What is pigmentation?
Pigmentation occurs in the skin when the underlying cells become damaged. This condition presents itself as discoloured patches of skin that are often darker in appearance to the surrounding skin. Age spots (also known as sunspots or solar lentigines) are common examples of this type of irregularity, which are more specifically referred to as hyperpigmentation.
When the areas of skin are lighter in appearance to the skin that surrounds it, this is known as hypopigmentation, which will often develop as a more widespread concern.
What are the causes?
Hyperpigmentation can occur on a variety of areas on the body, but it is more common for the face, neck, shoulders and hands to be affected. This is because sun exposure is the most likely cause. When UV rays penetrate the skin, melanin (the substance that gives your skin its colour) is produced to help protect the underlying cells. This can build-up gradually over a series of years to eventually form an isolated patch of darker skin tone. As this concern can take some considerable time to develop, it is mostly experienced by older adults, and is why it is often considered as being ageing-related.
When a person develops hypopigmentation, it is advisable to seek medical advice to rule out the possibility of any underlying health conditions.
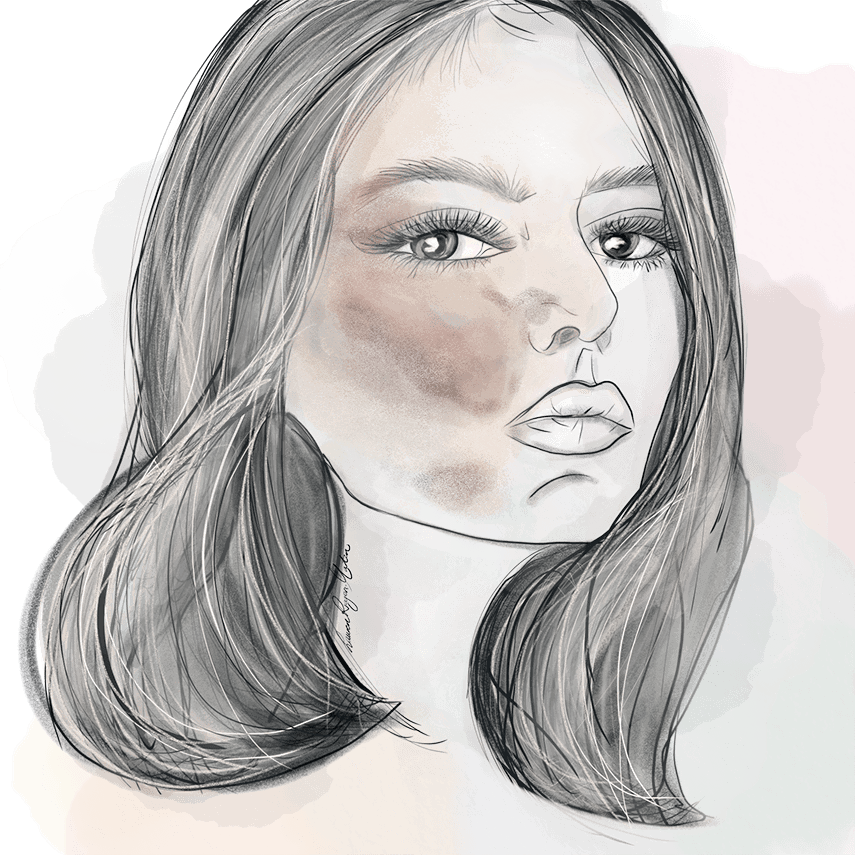
What is pigmentation?
Pigmentation occurs in the skin when the underlying cells become damaged. This condition presents itself as discoloured patches of skin that are often darker in appearance to the surrounding skin. Age spots (also known as sunspots or solar lentigines) are common examples of this type of irregularity, which are more specifically referred to as hyperpigmentation.
When the areas of skin are lighter in appearance to the skin that surrounds it, this is known as hypopigmentation, which will often develop as a more widespread concern.
What are the causes?
Hyperpigmentation can occur on a variety of areas on the body, but it is more common for the face, neck, shoulders and hands to be affected. This is because sun exposure is the most likely cause. When UV rays penetrate the skin, melanin (the substance that gives your skin its colour) is produced to help protect the underlying cells. This can build-up gradually over a series of years to eventually form an isolated patch of darker skin tone. As this concern can take some considerable time to develop, it is mostly experienced by older adults, and is why it is often considered as being ageing-related.
When a person develops hypopigmentation, it is advisable to seek medical advice to rule out the possibility of any underlying health conditions.